What is C-band?
The C-band is full band between 4 to 8GHz, which has been used for satellite since 1970s, now part of the band ranges is released for cellular companies.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has divided C-band into three groups: band n77(3300~4200MHz), band n78(3300~3800MHz), and band n79(4400~5000MHz).
Most European and Asian countries currently use n78(3.3 to 3.8GHz).
The USA uses n77(3.3 to 4.2GHz), it means carriers can combine 3.45GHz, CBRS, and C-band for wider channels if they have the licenses available.
Japan also already uses n77.
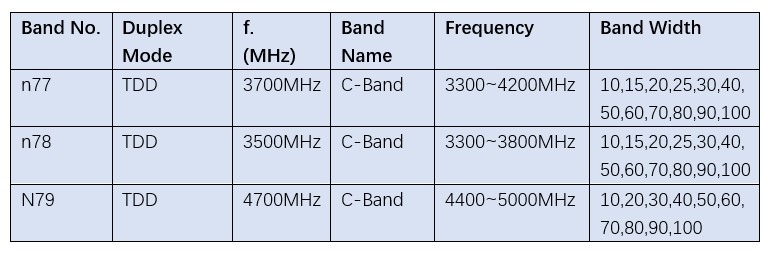
In many countries, n77 (3700 MHz), or commonly referred to as the 3.7 GHz 5G band, or C-band 5G, is the most commonly tested and deployed 5G frequency. The n77 band’s popularity is due to its relatively common availability, compared to lower cellular spectrum (below 2700MHz) already widely in use by 3G and 4G networks.
How C-band features?
The advanced testing technology:
For the lower frequency 5G bands, it is similar to 4G LTE. For example. The 5G low band 600MHz is similar on testing as 4G LTE, such as PIM and sweep testing.
But 5G installations are fiber infrastructure based instead of coaxial cabling.
When the band reach 3-3.5GHz or higher, technologies like beamforming and mmWave stand out and show its importance.
The comparison of interferences:
5G SA networks will still be subject to interference, but interference will be greatly reduced compared to 4G networks
4G LTE environment: there are many commonly used devices that operate over the same frequencies as mobile phones.
5G standalone: makes use of frequency bands that are not occupied by commonly used devices.
5G beamforming—a technology which also helps users avoid some types of interference. Beamforming is a signal processing technique that uses the multiple antennas available with massive MIMO to create a focused signal (or beam) between an antenna and specific user equipment. Signals can be controlled by modifying magnitude and phase, giving the ability for the antenna to focus on specific users.
It means that C-band is able to use technologies such as massive MIMO and beamforming to obtain superior signal coverage.
The bandwidth of C-band:
The C-band provides broad bandwidth from 50MHz to 100MHz commonly. It relieved the in-band congestion situation and make a big leap on the network speed.
In the daily work, when almost all the works are fulfilled via internet. Speed means everything.
The augmented reality (AR), Internet of Things technology (IoT), the online streamline or video interactive, 5G gaming etc., the faster the better.
When the C-band enters business innovation, it brings the lighting-fast speed to enhance satisfaction, maximize the benefits of 5G.
Connectivity over longer distances between cell towers:
The aim of 5G is always to run faster and travel longer distance.
When you want faster, you need to broaden the band much wider than 4G;
when the operators want the signals can travel at a decent range from towers, or to cover the full cities, they need to choose frequency below about 6GHz.
C-band is the answer of all above. That’s the “last mile“ we can call it in mobile connectivity.
In summary, combined with the bandwidth advantages of C-band, long-distance transmission ability, anti-interference performance and adopting advanced testing technology, C-band has become increasingly important in 5G applications.
Nowadays, 5G is no doubt offering extraordinary experiences on network speed, to achieve this, it requires broader band spectrum than its predecessors. That’s how C-band show up, which enhances the 5G development and brings to the network to full-wing fly.




